Treatment of nail fungus takes at least six months and is subject to properly prescribed treatment. Many people, especially on the eve of summer, worry about the question: how quickly will the nails return to their former healthy appearance? What will they look like immediately after starting treatment? And in a month or two?
Additionally, whether the treatment works or not can also be determined by the appearance of the nails. Let's see what you should pay attention to regarding the appearance of your nails after fungus treatment.
Why is nail fungus difficult to treat?
Onychomycosis (fungal infection of the nail plate) is very difficult to treat in everyone. There are three reasons for this:
The microbe penetrates the nail bed and not all local medications can reach it. In addition, most fungi provide themselves with "protection" in the form of thickening of the nail plate.
In most cases, onychomycosis is accompanied by a fungal infection of the foot. And as soon as a person heals his nails, the fungus again enters the nail bed from the skin of the foot.
Reinfection also occurs through own socks, shoes, as well as when bathing/showering.
Classic types of treatment for onychomycosis
Currently, medicine uses three main approaches to treat nail fungus:
Systemic medications in the form of tablets or capsules. They can help, but for this they must be followed over a long period of time - from 4 to 18 months. All of these medications are toxic to the liver and their intake can be complicated by the appearance of diarrhea, skin rashes and changes in taste. Therefore, during treatment, you must strictly follow a therapeutic diet, stop drinking alcohol and periodically take blood tests - "liver tests".
Local remedies (creams, varnishes). They do not always penetrate the nail plate well. It is therefore necessary to prepare it in advance: cut off the overgrown masses of the nail with a nail clipper or remove it using a cutter. You can't do it yourself: you can damage the cells that give rise to the nail plate.
Combined therapy: simultaneous administration of a systemic drug and application of a local antifungal agent to the affected nail. It is used in severe cases to slightly minimize the severity of side effects of systemic medications. The effectiveness of such treatment is also not very high.
In some cases, dermatologists remove the affected nail plate before prescribing topical treatment. Now they try to do this less and less, limiting themselves only to filing the affected area - in order to avoid infection of the nail bed with bacteria.
It would seem that onychomycosis can be left untreated, but in reality it represents much more than an aesthetic defect. It can cause a serious mixed infection (fungal and bacterial) of the foot or hand, which can even lead to gangrene.
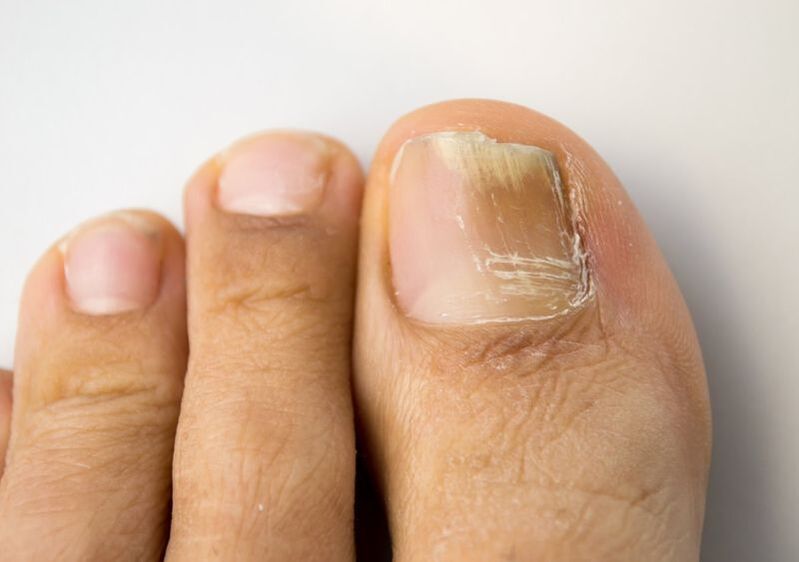
What do nails look like after fungus treatment?
In the first 2-3 months after the start of using local medications, the nail plate will not yet noticeably change. The fungi remaining in the subungual space continue to multiply and thickening or, conversely, thinning is again formed on the nail. The growing plaque retains its pathological color for some time: yellow, milky white, black or brown. It may still be scaly, ribbed or curved. There may be chips on it, or an area where it is moving away from its bed.
When treated with tablets, pathological changes in the growing nail plate can be observed for less than two months. Then, after treating the fungus, the area of the nail closest to the hole should return to a healthy appearance:
- become smooth;
- change color to pinkish or reddish, uniform in color;
- acquire a normal thickness.
If the nail grows back after removing the entire nail plate, it has the right to be a little thinner. It is also an indicator of one's health.
If, despite the treatment, after 2-3 months the nails remain altered in terms of color, thickness or softness, the treatment must then be reviewed.
How quickly the entire nail will become healthy
It depends on the growth rate of the nail plates. It is influenced by:
- age: the younger the person, the greater the speed;
- nature of nutrition: insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements reduces the rate of nail growth;
- Room temperature: In warm climates, nails grow faster;
- frequency of nail injuries: they slow down the growth of plates;
- hormonal status: for example, during pregnancy, the rate of plaque growth increases;
- the presence of common chronic diseases: they slow down the growth of nails;
- taking medications that affect the rate of cell division.
On average, a healthy nail after treating a fungus on the hands grows in 6 months, on the feet in 12-18 months. Thumb and toenails grow more slowly than others. So, if the nail plates of 2-5 fingers of the lower extremities grow at a speed of 1 mm/month, then on the first finger this speed can reach 0. 7 mm/month.
How to speed up the treatment of onychomycosis?
To speed up nail regrowth after fungus treatment, laser therapy can be used. It involves treating the nail plate with a neodymium laser device with a wavelength of 1064 nm. Its radiation freely penetrates the nail bed and heats fungal cells there to high temperatures, which leads to their death. Additionally, the heat from the laser activates blood circulation in the nail bed, which accelerates the growth of a healthy nail plate.
The laser is used in conjunction with local therapy. After a laser treatment session, the patient should apply the recommended cream or varnish to the nails, as well as carefully treat shoes with an antiseptic to avoid reinfection.
The effectiveness of treatment of onychomycosis with a neodymium laser has been tested in several foreign multicenter studies. It is an excellent complement to local treatment, has a short procedure duration and is not accompanied by side effects.
So, a healthy nail plate should begin to grow in the first months after starting treatment. It may be slightly thinner than usual, but have an even pinkish color and softness. The treatment process is significantly accelerated when the affected plates are treated with a neodymium laser.























